2004 – 2008 圣路易斯华盛顿大学能源环境与化学工程系,博士
2002 – 2004 清华大学环境科学与工程系,硕士
1998 – 2002 清华大学环境科学与工程系,学士
本站不再支持您的浏览器,360、sogou等浏览器请切换到极速模式,或升级您的浏览器到 更高版本!以获得更好的观看效果。关闭

师资队伍
首页 > 师资队伍 > 教师 > 大气污染与控制教研所 > 正文
大气污染与控制教研所
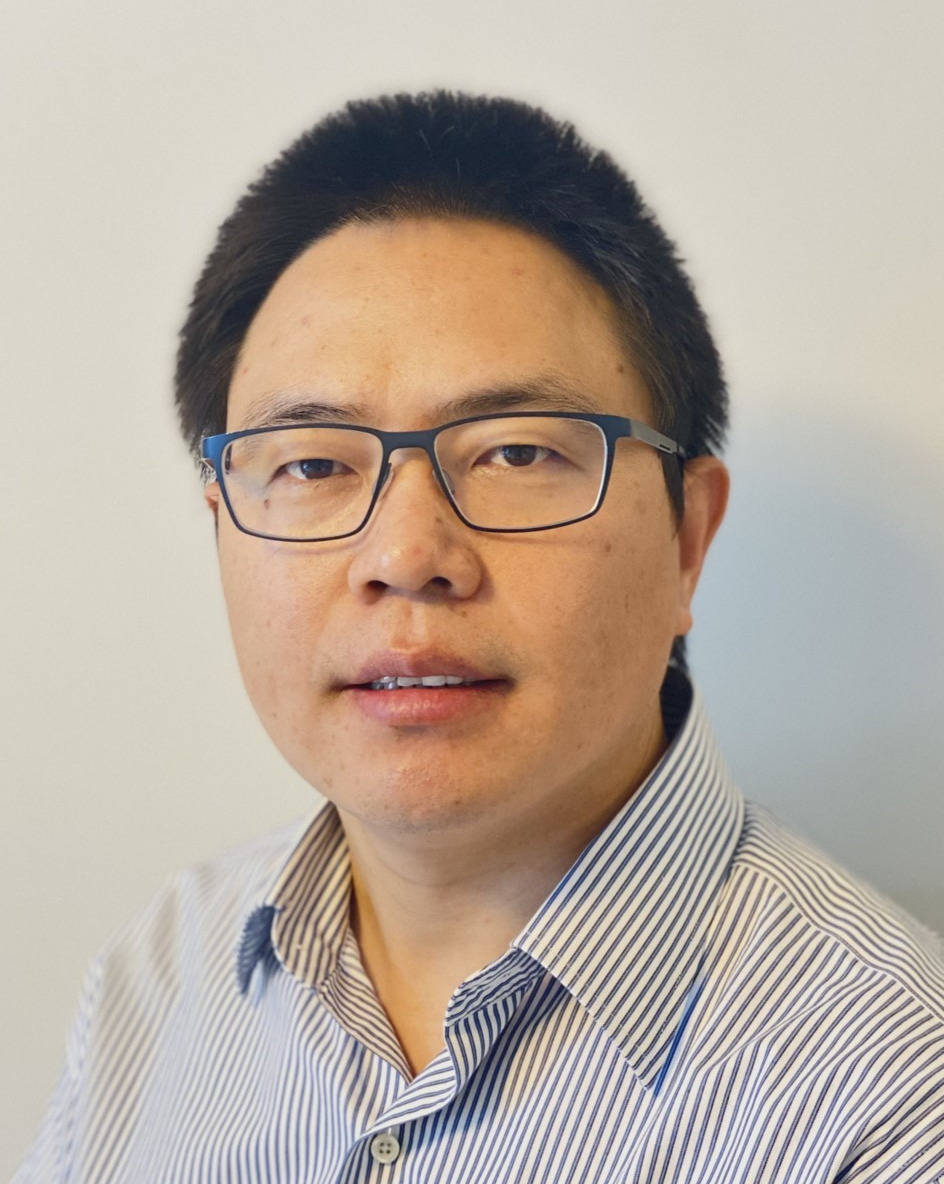

蒋靖坤
教授、科研院副院长
 邮 箱:jiangjk@tsinghua.edu.cn
邮 箱:jiangjk@tsinghua.edu.cn
 电 话:010-62781512
电 话:010-62781512
 地 点:清华大学中意清华环境节能楼
地 点:清华大学中意清华环境节能楼

教育背景
2004 – 2008 圣路易斯华盛顿大学能源环境与化学工程系,博士
2002 – 2004 清华大学环境科学与工程系,硕士
1998 – 2002 清华大学环境科学与工程系,学士

工作履历
2019-2023 清华大学环境学院 副院长
2017-至今 清华大学环境学院 长聘教授
2010-2016 清华大学环境学院 副研究员、准聘副教授、长聘副教授
2008 -2010 明尼苏达大学机械工程系,博士后
教学
2021-至今 理论与实践:空气(本科生)
2011-至今 气溶胶力学(研究生)
2013-2020 空气质量管理(本科生)
2020 新生导引课(本科生)
2010 纳米技术与工程,客座教师
2008 表面和胶体科学,助教
2005 传递现象,助教

学术兼职
2021 – 至今 Editorial Board, Results in Engineering
2020 – 至今 Editorial Board, Environmental Science & Technology Letters
2019 – 至今 Editorial Board, Environmental Research
2016 – 至今 Editor, Aerosol Science and Technology
2016 – 至今 环境模拟与污染控制国家重点联合实验室清华分室主任
2017 – 2018 Technical Program Committee, 2018 International Aerosol Conference
2017 – 2020 Guest editor, Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics
2016 – 2019 Editorial Board, Journal of Aerosol Science

奖励与荣誉
2020,ES&T Letters Excellence in Review Award
2020,教育部长江学者特聘教授
2019,中国化学会青年环境化学奖
2019,清华大学青年教师教学优秀奖
2019,清华大学先进工作者
2018,Smoluchowski Award
2017、2018、2019, 清华大学年度教学优秀奖
2016,教育部青年长江学者
2016,北京市科技进步一等奖
2016,国家环境保护专业技术青年拔尖人才
2016,清华大学2015届&2016届毕业生心目中的好教师
2015,Asian Young Aerosol Scientist Award
2015,国家科技进步二等奖
2014,“万人计划”青年拔尖人才
2014,教育部科技进步一等奖
2014,北京市科技新星
2012,清华大学第五届青年教师教学大赛二等奖(理工组)
2009,A&WMA Dissertation Award
2002,清华大学优良毕业生

研究领域
大气污染与控制、气溶胶科学与技术、生态环境监测

研究概况
大气多相全氧化态有机组分在线测量质谱仪研制,国家重大科研仪器研制项目,2024-2028
大气霾化学,基金委基础科学中心项目,2022-2026
固定源超低排放高精度监测与质控技术,国家重点研发计划,2022-2025
我国东部超大城市群大气复合污染成因外场综合协同观测研究,基金委重大研究计划集成项目,2021-2023
环境介质中的病毒识别与传播规律,基金委重大项目,2021-2025
新冠病毒传播与环境的关系及风险防控,国务院联防联控机制科技攻关专项,2020-2021
New particle formation and growth mechanism in atmospheric environments with high aerosol loading, Samsung Global Research Program, 2019-2025
面向交通系统颗粒物排放监测的道路微站技术研究,政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项,2019-2022
改进冷凝生长技术以提高1-3纳米大气颗粒物检测效率,基金委面上项目, 2019-2022
多尺度高时空分辨率污染物排放及变化趋势,国家重点研发计划,2018-2021
大气中Criegee中间体实时在线检测方法研发,基金委重点项目,2018-2022
纳米颗粒物粒径分析技术,国家重点研发计划,2017-2020
大气细颗粒物暴露导致慢阻肺的暴露组学与系统生物学研究,基金委重大研究计划重点项目,2017-2020
大气颗粒有机物在线前处理及富集技术研发,国家重点研发计划,2016-2020
大气污染化学,基金委优秀青年基金项目,2015-2017
长三角区域大气重污染事件发生特征与形成途径研究,“十二五”科技支撑项目,2014-2017
北京市民用燃煤PM2.5排放特征研究,北京市科技新星项目,2014-2017
多介质复合污染与控制化学,基金委创新群体项目,2013-2018
二次细粒子粒径分布、化学组成和光学特性在线测量系统,基金委国家重大科研仪器设备研制专项,2013-2017
烟气系统中细颗粒物的转化机制与脱除增强的机理与方法,973项目,2013-2017
钢铁窑炉烟尘PM2.5控制技术与装备,863项目,2013-2015
大气二次颗粒物的化学组分特征及形成机制,基金委重大项目,2012-2016
大气新粒子的生长机制研究, 基金委青年基金项目,2012-2014
长江三角洲地区大气灰霾特征与控制途径研究, 环保公益性行业科研项目,2010-2013
Clusters to Nanoparticles: Implications for Atmospheric Nucleation. U.S. National Science Foundation, 2005-2010
Growth Rates of Freshly Nucleated Particles. U.S. Department of Energy, 2007-2010
Relationship between Phsico-chemical Characteristics and Toxicological Properties of Nanomaterials. U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research, 2005-2009
Full Development of Interactive Aerosol Program. U.S. National Science Foundation, 2005-2008
Synthesis and Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles. U.S. National Science Foundation, 2003-2007
燃烧源可吸入颗粒物源的物理化学特征及其成因研究,973计划项目,2002-2007

部分学术成果
一、英文文章
(完整英文文章列表请点击链接查看。课题组招收本科生、研究生和博士后,欢迎联系jiangjk@tsinghua.edu.cn)
Sandwich-Structured ZnO/MXene Heterojunction for Sensitive and Stable Room-Temperature Ammonia Sensing[J]. Li, DL, Zhang, Z, Jiao, MZ, Dong, YN, Yu, SY, Li, CJ, He, HY, Jiang, JK, Liu, KH, Li, ZH. SMALL, Published 2025, Volume 21, Issue 11
Global variability in atmospheric new particle formation mechanisms[J]. Zhao, B, Donahue, NM, Zhang, K, Mao, LZ, Shrivastava, M, Ma, PL, Shen, JW, Wang, SX, Sun, J, Gordon, H, Tang, SQ, Fast, J, Wang, MY, Gao, Y, Yan, C, Singh, B, Li, ZQ, Huang, LY, Lou, SJ, Lin, GX, Wang, HL, Jiang, JK, Ding, AJ, Nie, W, Qi, XM, Chi, XG, Wang, L . NATURE, Published 2024, Volume 631, Issue 8019, Pages 98-105
The Significant Role of New Particle Composition and Morphology on the HNO3-Driven Growth of Particles down to Sub-10 nm[J]. Li, YY, Li, XX, Cai, RL, Yan, C, Zheng, GJ, Li, YR, Chen, YJ, Zhang, YS, Guo, YS, Hua, CJ, Kerminen, VM, Liu, YC, Kulmala, M, Hao, JM, Smith, JN, Jiang, JK. ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY, Published 2024, Volume 58, Issue 12, Pages 5442-5452
Precursor apportionment of atmospheric oxygenated organic molecules using a machine learning method
Qiao et al., Environmental Science: Atmospheres, 2023, 3 (1): 230-237
Increasing contribution of nighttime nitrogen chemistry to wintertime haze formation in Beijing observed during COVID-19 lockdowns
Yan et al., Nature Geoscience ,2023, 16 (11): 975-981
Achieving health-oriented air pollution control requires integrating unequal toxicities of industrial particles
Wu et al., Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 6491
Unified theoretical framework for black carbon mixing state allows greater accuracy of climate effect estimation
Wang et al., Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 2703
Online detection of airborne nanoparticle composition with mass spectrometry: Recent advances, challenges, and opportunities
Li et al., TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 166: 117195
Two pan-SARS-CoV-2 nanobodies and their multivalent derivatives effectively prevent Omicron infections in mice
Liu et al., Cell Reports Medicine, 2023, 4 (2): 100918
Single-atom catalysts: promotors of highly sensitive and selective sensors
Li et al., Chemical Society Reviews, 2023, 52 (15): 5088-5134
China’s public health initiatives for climate change adaptation
Ji et al., The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, 2023, 40: 100965
Secondary organic aerosol formed by condensing anthropogenic vapours over China's megacities
Nie et al., Nature Geoscience, 2022, 15: 255-261
Toxic potency-adjusted control of air pollution for solid fuel combustion
Wu et al., Nature Energy, 2022, 7: 194-202
The missing base molecules in atmospheric acid–base nucleation
Cai et al., National Science Review, 2022, 9 (10): nwac137
Application of smog chambers in atmospheric process studies
Chu et al., National Science Review, 2022, 9: nwab103
Liquid-liquid phase separation reduces radiative absorption by aged black carbon aerosols
Zhang et al., Communications Earth & Environment, 2022, 3 (1): 128
Cr-Doped Pd Metallene Endows a Practical Formaldehyde Sensor New Limit and High Selectivity
Zhang et al., Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(2): 2105276
Observation and Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Alkaline Gases in Urban Beijing
Zhu et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(24): 17545-17555
Ecological Barrier Deterioration Driven by Human Activities Poses Fatal Threats to Public Health due to Emerging Infectious Diseases
Zhang et al., Engineering, 2022, 10: 155-166
Measuring size distributions of atmospheric aerosols using natural air ions
Li et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2022, 56: 655-664
Emissions of Ammonia and Other Nitrogen-Containing Volatile Organic Compounds from Motor Vehicles under Low-Speed Driving Conditions
Yang et al., Environ. Sci. & Technol., 2022, 56: 5440-5447
Evaluation of a cost-effective roadside sensor platform for identifying high emitters
Shen et al., Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 816: 151609
Sulfuric acid-amine nucleation in urban Beijing
Cai et al., Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2021, 21(4): 2457-2468
Acid–Base Clusters during Atmospheric New Particle Formation in Urban Beijing
Yin et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55: 10994-11005
Contribution of Atmospheric Oxygenated Organic Compounds to Particle Growth in an Urban Environment
Qiao et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55: 13646-13656
An indicator for sulfuric acid–amine nucleation in atmospheric environments
Cai et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2021, 55: 1059-1069
Composition of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Beijing: Measurement Using a Thermal Desorption Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer
Li et al., Environmental science & technology, 2021, 55(5): 2859-2868
Improving data reliability: A quality control practice for low-cost PM2.5 sensor network
Qiao et al., Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 779: 146381
Seasonal Characteristics of New Particle Formation and Growth in Urban Beijing
Deng et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54: 8547-8557
Quantifying the Deposition of Airborne Particulate Matter Pollution on Skin Using Elemental Markers
Morgan et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(24): 15958-15967
Air pollutant emissions from coal-fired power plants in China over the past two decades
Wang et al., Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140326
Transmission via aerosols: Plausible differences among emerging coronaviruses
Jiang et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2020, 54: 865-868
Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry with a solid-state thermal modulator for in-situ speciated measurement of organic aerosols
An et al., Journal of Chromatography A, 2020, 1625: 461336
Evaluating Airborne Condensable Particulate Matter Measurement Methods in Typical Stationary Sources in China
Wang et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54: 1363-1371
Significant ultrafine particle emissions from residential solid fuel combustion
Wang et al., Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 715, 136992
Models for estimating nanoparticle transmission efficiency through an adverse axial electric field
Cai et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2020, 54: 332-341
Transmission of charged nanoparticles through the DMA adverse axial electric field and its improvement
Cai et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2020, 54: 21-32
Cobalt Nanoparticles and Atomic Sites in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Frameworks for Highly Sensitive Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide
Li et al., Small, 2020, 16: 1902860
Theoretical and experimental analysis of the core sampling method: Reducing diffusional losses in aerosol sampling line
Fu, et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2019, 53: 793-801
A soft X-ray unipolar charger for ultrafine particles
Chen et al., Journal of Aerosol Science, 2019, 133: 66-71
Improving thermal desorption aerosol gas chromatography using a dual-trap design
Ren et al., Journal of Chromatography A, 2019, 1599: 247-252
Quartz filter-based thermal desorption gas chromatography mass spectrometry for in-situ molecular level measurement of ambient organic aerosols
Ren et al., Journal of Chromatography A, 2019, 1589: 141-148
Relative humidity effect on the formation of highly oxidized molecules and new particles during monoterpene oxidation
Li, et al., Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 19: 1555-1570
Characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter emitted from two waste incineration power plants in China
Wang et al., Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 695-704
Stationary characteristics in bipolar diffusion charging of aerosols: Improving the performance of electrical mobility size spectrometers
Chen et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2018, 52: 809-813
Retrieving the ion mobility ratio and aerosol charge fractions for a neutralizer in real-world applications
Chen et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2018, 52: 1145-1155
Data inversion methods to determine sub-3 nm aerosol size distributions using the particle size magnifier
Cai et al., Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2018, 11: 4477-4491
Nascent soot particle size distributions down to 1 nm from a laminar premixed burner-stabilized stagnation ethylene flame
Tang et al., Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36: 993-1000
Aerosol surface area concentration: a governing factor in new particle formation in Beijing
Cai et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2017, 17: 12327-12340
A new balance formula to estimate new particle formation rate: reevaluating the effect of coagulation scavenging
Cai et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2017, 17: 12659-12675
A miniature cylindrical differential mobility analyzer for sub-3 nm particle sizing
Cai et al., Journal of Aerosol Science, 2017, 106: 111-119
Evolution of Submicrometer Organic Aerosols during a Complete Residential Coal Combustion Process
Zhou et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50: 7861-7869
A spectrometer for measuring particle size distributions in the range of 3 nm to 10 μm
Liu et al., Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2016, 10: 63-72
Gaseous Ammonia Emissions from Coal and Biomass Combustion in Household Stoves with Different Combustion Efficiencies
Li et al., Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2016, 3: 98-103
Optimized DNA extraction and metagenomic sequencing of airborne microbial communities
Jiang et al., Nature Protocols, 2015, 10: 768
Laboratory Evaluation and Calibration of Three Low-Cost Particle Sensors for Particulate Matter Measurement
Wang et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2015, 49: 1063-1077
Aerosol Charge Fractions Downstream of Six Bipolar Chargers: Effects of Ion Source, Source Activity, and Flowrate
Jiang et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2014, 48: 1207-1216
Inhalable Microorganisms in Beijing’s PM2.5 and PM10 Pollutants during a Severe Smog Event
Cao et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48: 1499-1507
Characteristics and health impacts of particulate matter pollution in China (2001–2011)
Cheng et al., Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 65: 186-194
Mobility particle size spectrometers: harmonization of technical standards and data structure to facilitate high quality long-term observations of atmospheric particle number size distributions
Wiedensohler et al., Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2012, 5: 657-685
Acid-base chemical reaction model for nucleation rates in the polluted atmospheric boundary layer
Chen et al., PNAS, 2012, 109: 18713-18718
Role of Surface Area, Primary Particle Size, and Crystal Phase on Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Dispersion Properties
Suttiponparnit et al., Nanoscale Research Letters, 2011, 6:
First Measurements of Neutral Atmospheric Cluster and 1–2 nm Particle Number Size Distributions During Nucleation Events
Jiang et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2011, 45: ii-v
Electrical Mobility Spectrometer Using a Diethylene Glycol Condensation Particle Counter for Measurement of Aerosol Size Distributions Down to 1 nm
Jiang et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2011, 45: 510 - 521
Transfer Functions and Penetrations of Five Differential Mobility Analyzers for Sub-2 nm Particle Classification
Jiang et al., Aerosol Science and Technology, 2011, 45: 480 - 492
Ambient Pressure Proton Transfer Mass Spectrometry: Detection of Amines and Ammonia
Hanson et al., Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45: 8881-8888
Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies
Jiang et al., Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2009, 11: 77-89
Does nanoparticle activity depend upon size and crystal phase?
Jiang et al., Nanotoxicology, 2008, 2: 33 - 42
Model for nanoparticle charging by diffusion, direct photoionization, and thermionization mechanisms
Jiang et al., Journal of Electrostatics, 2007, 65: 209-220
Synthesis of nanoparticles in a flame aerosol reactor with independent and strict control of their size, crystal phase and morphology
Jiang et al., Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 285603
Anthropogenic mercury emissions in China
Streets et al., Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39: 7789-7806
中文文章
李晓晓, 蒋靖坤, 王东滨, 葛茂发, 郝吉明. 大气超细颗粒物来源及其化学组分研究进展. 环境化学, 2021, 40(10): 2947-2959.
李雪, 蒋靖坤*, 王东滨, 邓建国, 贺克斌, 郝吉明. 冠状病毒气溶胶传播及环境影响因素. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3091-3098.
王东滨, 薛墨, 陈小彤, 蒋靖坤*. 一种新型软X射线气溶胶荷电器的开发与评测. 大气与环境光学学报, 2020, 15(06): 429-437.
张莹,邓建国,王刚,李妍菁,续鹏, 蒋靖坤*,典型钢铁焦化厂可凝结颗粒物排放特征,环境工程,2020, 38(09): 154-158.
邓建国, 张莹, 王乐冰, 李妍菁, 段雷, 郝吉明, 蒋靖坤*,测量固定源可凝结颗粒物的稀释间接法及系统,环境科学学报,2020,40(11):4162-4168.
楚碧武, 马庆鑫, 段凤魁, 马金珠, 蒋靖坤, 贺克斌, 贺泓. 大气“霾化学”:概念提出和研究展望. 化学进展, 2020, 32: 1-4.
蒋靖坤*,邓建国,王刚,张莹,李妍菁,段雷,郝吉明.固定污染源可凝结颗粒物测量方法.环境科学, 2019, 40(12): 5234-5239.
王东滨, 郝吉明, 蒋靖坤*. 民用固体燃料燃烧超细颗粒物排放及其潜在健康影响. 科学通报, 2019, 64: 3429.
邓建国,马子轸,李振,段雷,蒋靖坤*.不同湿法脱硫工艺对燃煤电厂PM2.5排放的影响.环境科学,2019,40(8):3457-3462.
姚群, 柳静献, 蒋靖坤. 钢铁窑炉烟尘细颗粒物超低排放技术与装备. 中国环保产业, 2018, 6: 39 – 43.
李庆, 段雷, 蒋靖坤*, 王书肖, 郝吉明. 我国民用燃煤一次颗粒物的减排潜力研究. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 16: 4408-4414
樊筱筱, 蒋靖坤*, 吴烨, 张强, 李振华, 段雷. 不同稀释条件与测量技术下缸内直喷汽车排放颗粒物数浓度和粒径分布特征. 中国电机工程学报,2016, 16
樊筱筱, 蒋靖坤*, 张强, 李振华, 何立强, 吴烨, 胡京南, 郝吉明. 轻型汽油车排放颗粒物数浓度和粒径分布特征. 环境科学,2016, 37(10): 3743-3749
蒋靖坤*, 邓建国, 李振, 马子轸, 周伟, 张强, 段雷, 郝吉明. 双级虚拟撞击采样器应用于固定污染源PM10和PM2.5排放测量. 环境科学,2016, 37(6): 2003-2007
张琦, 李庆, 蒋靖坤*, 邓建国, 段雷, 郝吉明. 一套民用固体燃料燃烧大气污染物排放测试系统的搭建和评测. 环境科学学报,2016,36:3393-3399
陈小彤, 蒋靖坤*, 邓建国, 李庆, 段雷,郝吉明. 一种气溶胶测量仪器标定系统的设计及性能评估. 环境科学,2016, 37(3): 789-794
马子轸, 李振, 蒋靖坤, 叶芝祥, 邓建国, 段雷. 燃煤电厂产生和排放的PM2.5中水溶性离子特征. 环境科学, 2015, 36(7):2361-2366
王步英, 郎继东, 张丽娜, 方剑火, 曹晨, 郝吉明, 朱听, 田埂*, 蒋靖坤*. 基于16S rRNA基因测序法分析的北京霾污染过程PM2.5和PM10中细菌群落特征. 环境科学, 2015, 36(8): 2727-2734
段雷, 马子轸, 李振, 蒋靖坤, 叶芝祥. 燃煤电厂排放细颗粒物的水溶性无机离子特征综述. 环境科学, 2015, 36(3): 1117-1122
蒋靖坤*, 邓建国, 段雷, 张强, 李振, 陈小彤, 李兴华, 郝吉明. 基于虚拟撞击原理的固定源PM10/PM2.5采样器的研制. 环境科学, 2014, 35(10): 3639-3643.
蒋靖坤*, 邓建国, 李振, 李兴华, 段雷, 郝吉明. 固定污染源排气中PM2.5采样方法综述. 环境科学, 2014,35(5): 2018-2024.
麦华俊, 蒋靖坤*, 何正旭, 郝吉明. 一种纳米气溶胶发生系统的设计及性能测试. 环境科学, 2013,34: 2950-2954
蒋靖坤, 郝吉明, 吴烨, David G. Streets, 段雷, 田贺忠. 中国燃煤汞排放清单的初步建立. 环境科学, 2005, 26: 34-39.
地址 : 北京市海淀区清华大学环境学院
邮编 : 100084
邮箱 : hjx@tsinghua.edu.cn
电话 : +86-10-62784521
传真 : +86-10-62785687

环境学院公众号

本科生公众号

研究生公众号
Copyright © 2017 清华大学环境学院 版权所有
